Table of Contents
What is a Cab Card in Trucking
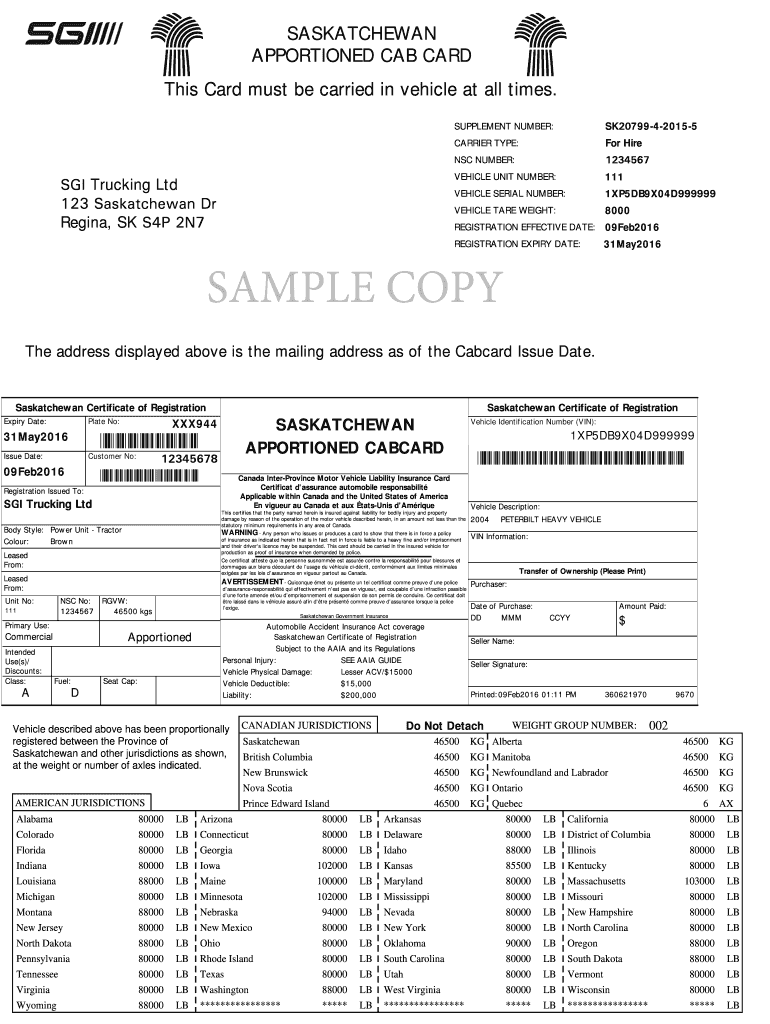
Cab card is a document that serves as proof of registration and allows a commercial motor vehicle to operate across multiple jurisdictions (states or provinces) under the apportioned registration system – International Registration Plan.
Learn more about International Registration Plan IRP here.
This article is currently being updated.
The cab card contains essential information about the vehicle’s apportioned registration, which includes the following details:
Vehicle Information: The cab card includes information about the registered vehicle, such as its make, model, vehicle identification number (VIN), and license plate number.
Registered Jurisdictions: The cab card lists the member jurisdictions (states or provinces) where the vehicle is authorized to operate under its apportioned registration.
Apportioned Weight: This section provides the registered gross vehicle weight or the registered gross combination weight for the vehicle, which is used for calculating the apportioned fees.
Registration Period: The cab card indicates the start and end dates of the registration period for which the vehicle is authorized to operate under the IRP.
Apportioned Fees: Information about the fees paid for apportioned registration is typically displayed on the cab card, including the amount and how the fees are distributed among the registered jurisdictions.
Carrier Information: The name and address of the carrier or the registrant responsible for the vehicle’s registration are often included on the cab card.
Expiration Date: The cab card includes the expiration date of the apportioned registration. This is the date by which the vehicle’s registration must be renewed to maintain its eligibility for operation under the IRP.
Electronic Cab Cards
While electronic cab cards offer numerous benefits, their adoption and acceptance can vary among different jurisdictions and regulatory agencies. Some jurisdictions may require physical copies of documents, while others are more open to electronic formats. Carriers should ensure that their chosen electronic cab card solution meets the requirements of the jurisdictions in which they operate.
Convenience: Electronic cab cards are stored digitally, eliminating the need for physical paperwork. This streamlines record-keeping and reduces the risk of losing or damaging paper documents.
Real-Time Updates: Electronic systems can provide real-time updates and changes to registration information. This ensures that the information on the cab card is always accurate and up-to-date.
Ease of Access: Drivers and carriers can access electronic cab cards via smartphones, tablets, or other devices. This allows for quick presentation of the required documentation during inspections or when crossing jurisdictional borders.
Reduced Administrative Burden: Electronic cab card systems can automate processes such as renewals and fee calculations, reducing the administrative workload for carriers.
Integration: Electronic cab card systems can be integrated with other fleet management software, making it easier to manage various aspects of the trucking operation in one place.
Link to FMCSA PRISM IRP Cab Card Bar Code Specifications – Version 3.5
Cab Card Example